Let’s understand Large Language Model from scratch
Generative Model
Overview
In this blog, I am going to summary the 5 most common generative models: Auto-Regreesive Model, Variational AutoEncoder, Engery Based Model, Flow Model and Diffusion Model. I will also display the pros and cons between different models, and how we can combine those models to get better performance
What is the Large Language Model
Building Blocks of LLM
Same as other models, there are different building blocks for the LLM. Let’s break it down bottom up:
- Tokenization: Convert words into digits
- Embedding: Convert digits into the format that neural network can understand
- Neural Network: The Transformer neural network architecture of the LLM.
- Loss Function: The Cross Entropy Loss is the most common loss function when training LLM
- Optimizer: Most of the LLM is optimized by the AdamW.
- Parallelism: The Large Lanuage Model is larger, which means it hard to fit into the a single machine.
- Inference: After we have trained the model, we need to deploy it to use. However, due to the computing and memory demanding of the LLM. The inference time is slow.
- Evaluation: We need some metrics to measure how well the LLM is doing, and compare between different LLMs.
Tokenization
Word Level
Byte-Pair-Encoding
Bit Encoding
Embedding
Embedding is
Nerual Network Architecture
We are going to do the architecture based on Transformer,
Position Encoding
Normalization
Layer Normalization
RMS Normalization
Post-Norm vs. Pre-Norm
Without Normalization
Recently, (Zhu et al. 2025) proposed that we can remove the normalization without harm the performance of the neural network. It replace the normalization layer with a scaled tanh function, named Dynamic Tanh, defined as:
\[ \text{DyT}(x) = \gamma * \tanh(\alpha x) + \beta \tag{1}\]
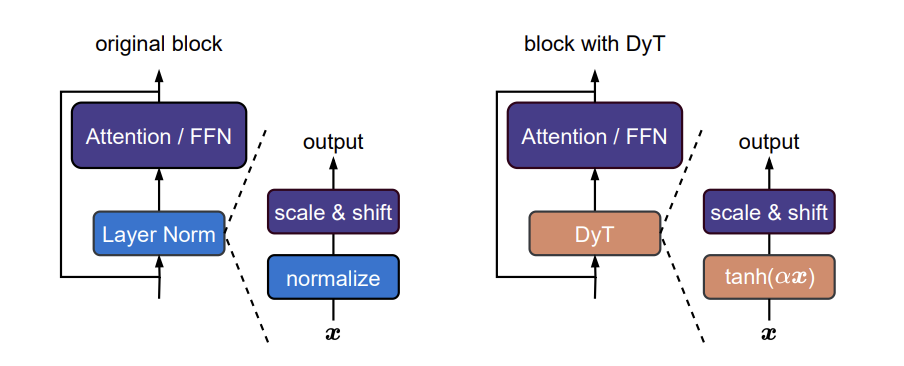
It adjust the input activation range via a learnable scaling factor \(\alpha\) and then squashed the extreme values through an S-shaped tanh function.
Attention Mechnism
Feed Forward Network
Mixture of Expert
Loss Function
Similar as the other training process, we need a loss function to training and tuning our parameters.
Cross Entropy Loss
Training
Model Initilization
Optimizer
About Gradients
Gradient Accumulations
Gradiant Clipping
Mixed Precision
Parallellism
Tuning
Supervised-Fine-Tuning
Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback
PPO
DPO
GRPO
Inferrence
Quantization
Knowledge Distillation
Evaluation
Fine-Tuning LLM
Prompt Enginnering
Prefix-Tuning
Adapter
LoRA
Q-LoRA
Multi Modality of LLM
Applications of LLM
ChatBot
Most know ChatGPT,
AI Agent
LLM as Optimizer
Zhu, Jiachen, Xinlei Chen, Kaiming He, Yann LeCun, and Zhuang Liu. 2025. “Transformers Without Normalization.” March 13, 2025. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2503.10622.